Let us calculate the number of parameters for bi-gram hMM given as
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \[p(x, y)=p(x|y)p(y)\,=\,\prod_{t=1}^{T}p(x_{t}|y_{t})p(y_{t}|y_{t-1})\]](https://machinelearninginterview.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-da9e1e96bca390bd552f19abd2ecce7a_l3.png)
Let ![]() be the total number of states
be the total number of states ![]() and
and ![]() be the vocabulary size and
be the vocabulary size and ![]() be the length of the sequence
be the length of the sequence
- Before directly estimating the number of parameters, let us first try to see what are the different probabilities or rather probability matrix we have.
- Once we know the probability matrix, we can estimate the parameters by its size.
- If you’re thinking how does a probability matrix appear, notice that we have conditional probabilities here,
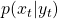 and
and 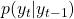 or probability expression involving 2 variables
or probability expression involving 2 variables  and
and  such as
such as 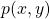 , hence we should have the probability matrix.
, hence we should have the probability matrix. - So for
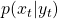 we have a probability matrix where each row
we have a probability matrix where each row 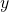 is a state and each column is an output variable
is a state and each column is an output variable 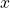 . Hence this matrix is of size
. Hence this matrix is of size  leading to these many parameters.
leading to these many parameters. - Similarly for
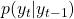 , we have
, we have 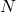 x
x 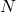 matrix and hence same number of parameters.
matrix and hence same number of parameters. - From (d) and (e), we have at least
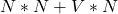 parameters.
parameters. - Now think carefully if we there is anything which we missed in our calculation.
- We also have start tokens
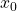 and initial state
and initial state 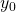 . In State Probability matrix explained in (e), we have one more row but columns are still N. Therefore number of parameters due to initial state
. In State Probability matrix explained in (e), we have one more row but columns are still N. Therefore number of parameters due to initial state 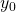 becomes
becomes 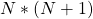
- Once you’re convinced, you’ll get to know that total number of parameters in the above hMM model are
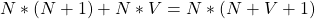
- Give a try for a general
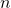 for n-gram hMM!
for n-gram hMM!