Python is compiled into bytecode (pyc file) and then interpreted- making it slower than languages such as C/C++ that are directly compiled. Cython is a tool to write compiled C extension for python to speed up code. Cython is easy to use and often leads to significant improvement in runtime.
In this article, lets walk through a simple python example to see how cython can speed up runtime for python code. The code for this video can be found here on girhub.
This example walks through a simple task of series sum, i.e finding the sum of the elements of a series.
def series_sum(x):
f = 0
for i in range(1, x+1):
f += i
return f
print(series_sum(10))
5
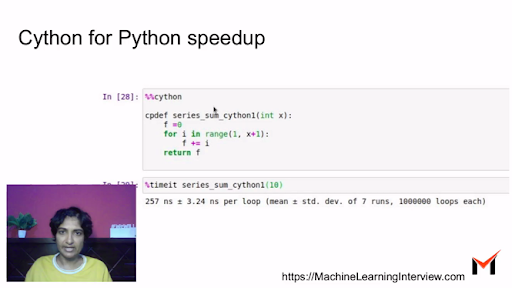
To measure the time taken to execute this function, one can run timeit that computes the average execution time of the function over a number runns.
%timeit series_sum(10) 452 ns ± 16.2 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000000 loops each)
How to write a Cython function in Python?
%cython -a cpdef int series_sum_cython(int x): cdef int f =0 cdef int i for i in range(1, x+1): f += i return f
%timeit series_sum_cython(10) 38.4 ns ± 0.291 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000000 loops each)
Python is a dynamically typed language. While this makes it very convenient in terms of scripting code really fast, it is less efficient since the type of a variable is not known in advance. We note how type information is provided in cython function.
Finally the cython function can be timed using timeit – and we see that there is a 10x difference in runtime between the original series sum function and the cython function.